Autonomous Parafoil Guidance & Control System
A custom PCB-based GNC system for precision payload recovery.
Project Overview
This project involved designing, building, and validating an autonomous guidance unit (AGU) capable of navigating a 5kg payload to a designated GPS coordinate. The system was designed to address the problem of recovering high-altitude scientific payloads, which often drift off-course during descent.
The final system features a custom 4-layer PCB, a high-fidelity sensor suite, and a robust Guidance, Navigation, and Control (GNC) algorithm. During final field testing, the system successfully navigated from a drop height of 75 meters to land within 5 meters of the target coordinate.
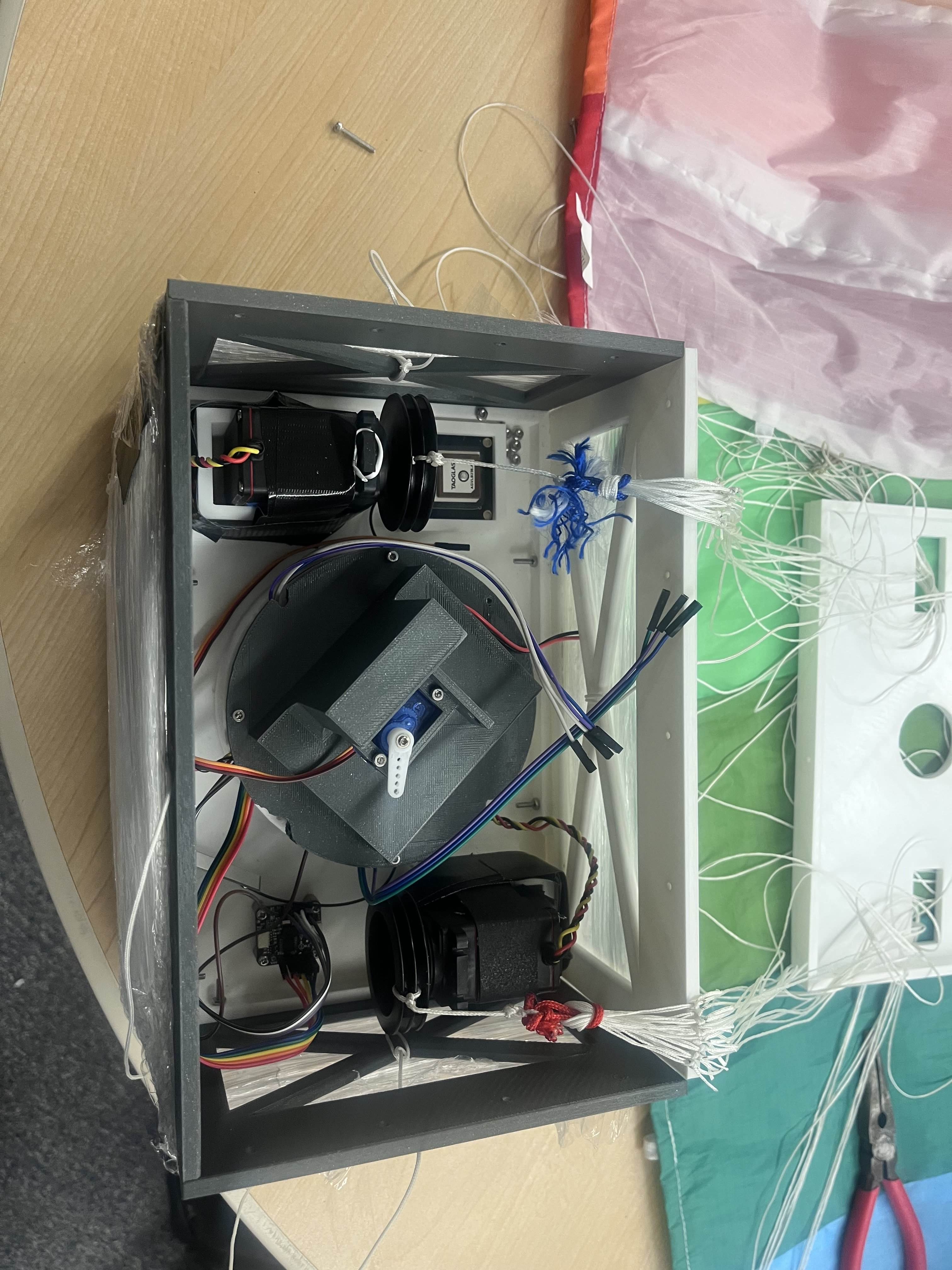

The final AGU assembly showing the servo actuation system and parachute rigging.
Flight Demonstration
On December 6, 2025, the system was validated in a live field test. Despite winter conditions, the AGU successfully steered the parafoil to the target landing zone.
Autonomous Descent
Altitude: 75m Drop
Action: The AGU detects freefall, deploys the parafoil, and begins actuating control lines to correct heading against the wind.
Precision Landing
Result: < 5m from target center.
Outcome: Successful autonomous flare and touchdown, followed by team celebration.
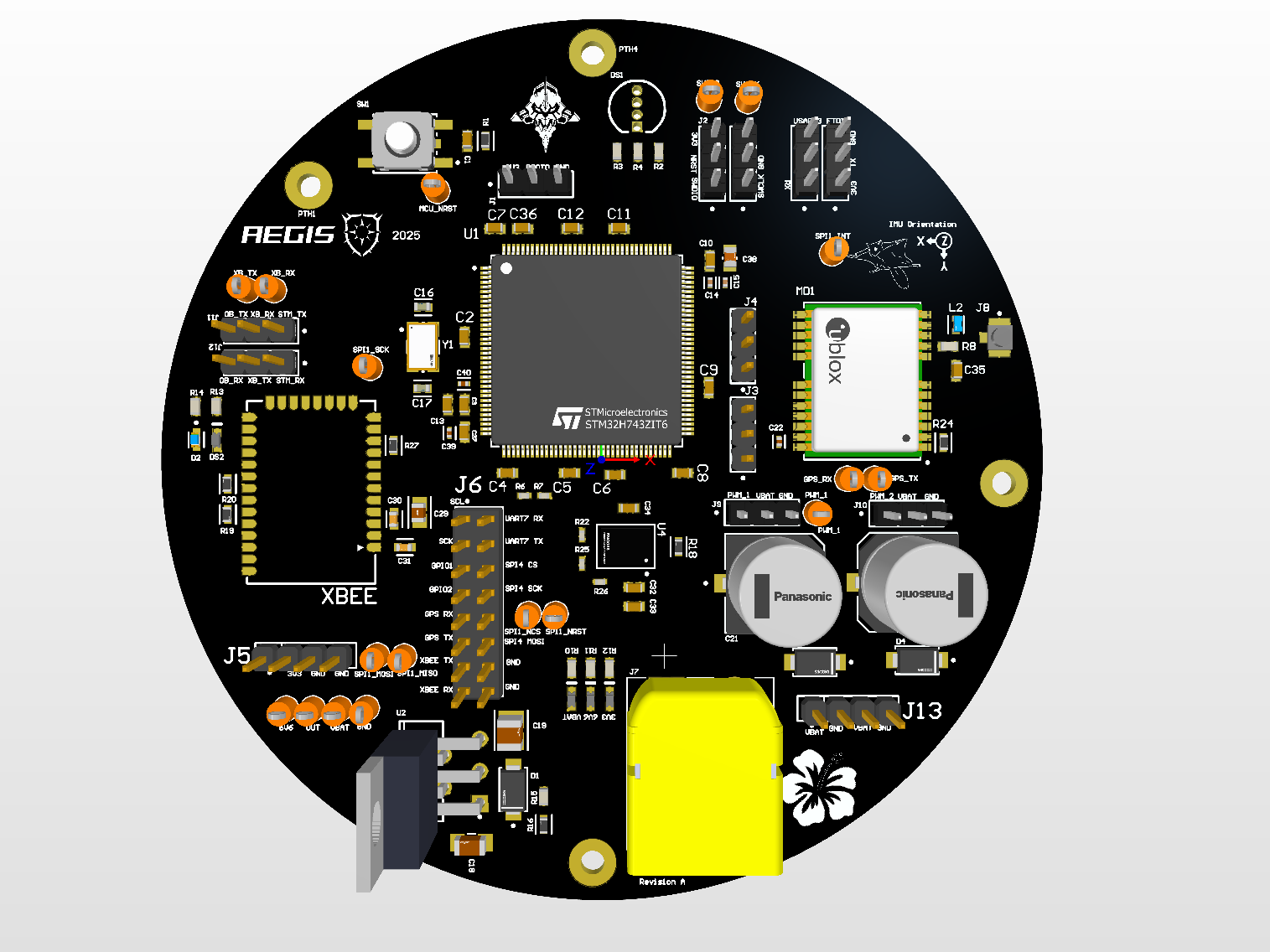
Custom PCB Architecture
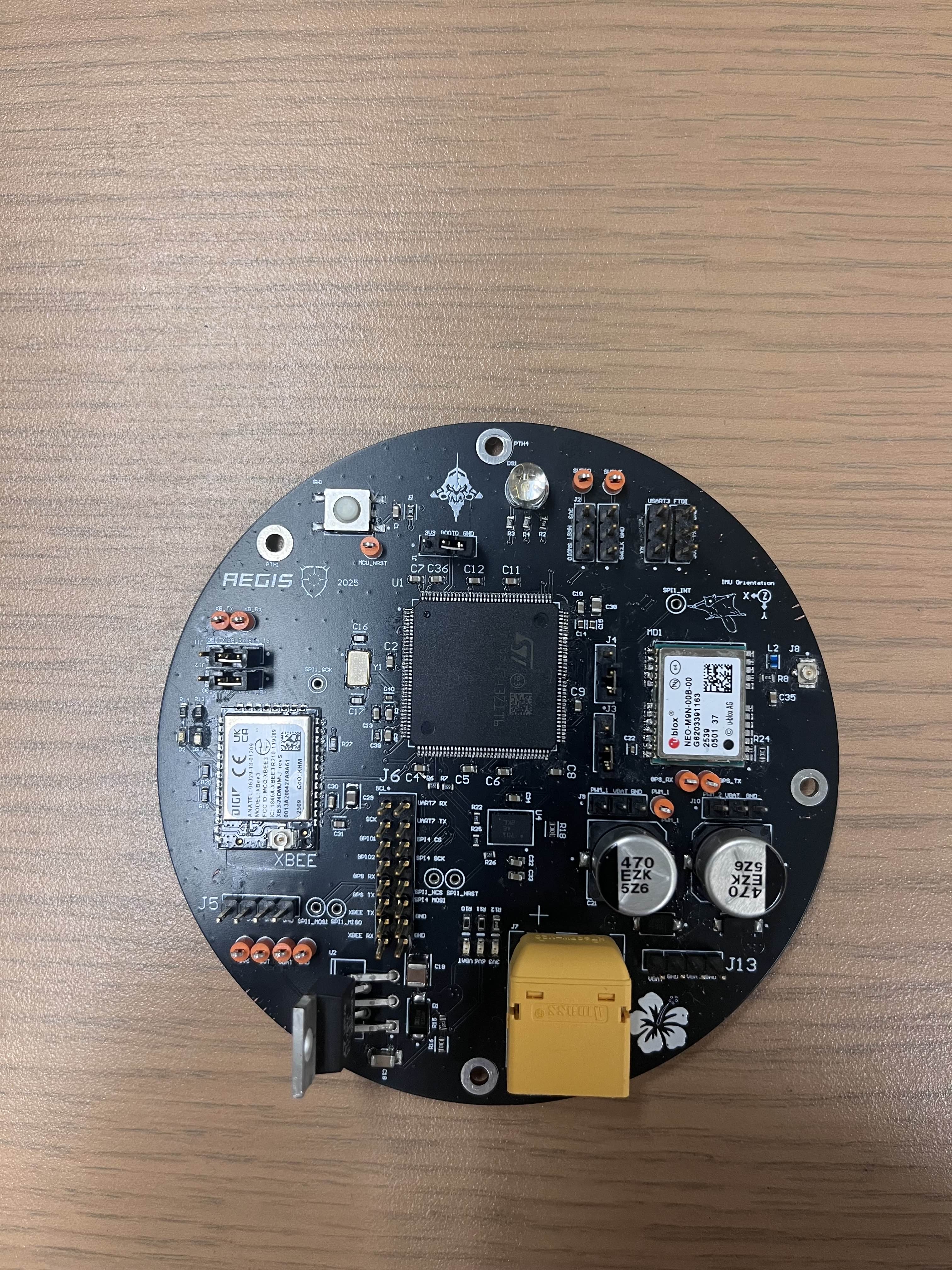


Click any image to enlarge
Layer Stackup & Signal Integrity
Designed a custom 4-layer PCB in Altium Designer using a Ground-Signal-Power-Ground stackup. This configuration shields sensitive internal signal traces from external EMI, crucial for the high-frequency GPS and RF modules. I utilized 2oz copper for internal layers to handle high current density from the servo motors and minimize resistive heating.
Power Distribution Network
Implemented a "Star Routing" topology to isolate the noisy high-current servo power rails from the sensitive 3.3V logic rails. This prevents voltage drops and ground bounce caused by servo stall currents from resetting the microcontroller.
RF & Component Integration
- MCU: STM32H7 High-Performance Microcontroller.
- GPS: Integrated NEO-M9N module with a custom bias-tee circuit (27nH inductor + 100nF cap network) to inject DC power into the active antenna while isolating the RF path.
- Sensors: BNO085 9-Axis IMU for attitude estimation.
- Protection: Reverse polarity protection via Schottky diodes and dedicated status LEDs for all power rails.
Firmware & Autonomy
FreeRTOS Architecture
The firmware operates on an STM32H7, utilizing FreeRTOS to manage the asynchronous nature of sensor data. The system is architected into three primary prioritized tasks:
- Startbno085 (High Priority): Polls IMU data at 100Hz via a custom SPI driver. It handles the SHTP protocol's fragmentation and reassembly to ensure zero data loss.
- readGPS (DMA-Driven): Parses binary UBX GPS packets using Direct Memory Access (DMA). This allows extraction of precise velocity vectors without blocking the CPU, unlike standard NMEA parsing.
- Telemetry & Control: Manages XBee communication and servo PWM generation in a lower-priority thread to maintain control loop stability.
Extended Kalman Filter (EKF)
I implemented a 7-state EKF (tracking Position N/E/D, Velocity N/E/D, and Heading Bias) to fuse the 100Hz inertial data with lower-frequency GPS updates. To optimize for the microcontroller, I developed a Sequential Update method, processing GPS scalars independently to avoid computationally expensive 7x7 matrix inversions.
Safety Systems
Includes a "Deadspin" failsafe mode that forces a spiral descent if critical sensors fail or the geofence is breached.
System Control Loop
100Hz Real-Time Execution
State Estimation
Path Planning